MySQL is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) widely used for storing, managing, and retrieving structured data. It is based on Structured Query Language (SQL), which is used to interact with the database through commands such as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE. MySQL is developed, distributed, and supported by Oracle Corporation and is known for its speed, reliability, and ease of use.
MySQL organizes data into one or more tables, each consisting of rows and columns, making it ideal for applications where data integrity and relationships are crucial, such as web applications, e-commerce platforms, and content management systems. It supports multiple storage engines, transactions, stored procedures, triggers, and views, enhancing its flexibility and functionality
One of MySQL’s key advantages is its cross-platform support and ability to handle large databases with high performance. It is often used with programming languages such as PHP, Python, or Java and commonly runs on web servers like Apache or Nginx
With features like security through user privileges, data encryption, and replication for backup and scaling, MySQL remains a trusted solution for developers and businesses worldwide. Its widespread adoption in platforms like WordPress, Facebook, and Twitter demonstrates its robustness and scalability.
First we’re going to take a look at a general steps to establish a PHP MySQL connection. And after that, we’ll check out how to PHP MySQL connect using php
What we’re doing: Setting up a local server environment
1. XAMPP (Recommended) – A local server that includes PHP, MySQL, and Apache
2. phpMyAdmin – A web-based MySQL database management tool (included with XAMPP)
3. A Code Editor – Such as VS Code, Sublime Text, or Notepad++.
Download XAMPP from Apache Friends
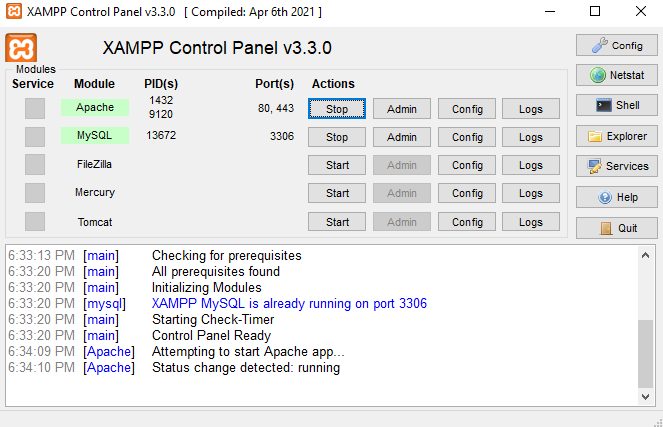
Install XAMPP and start Apache and MySQL from the XAMPP Control Panel.

If you see green indicators, everything is running fine
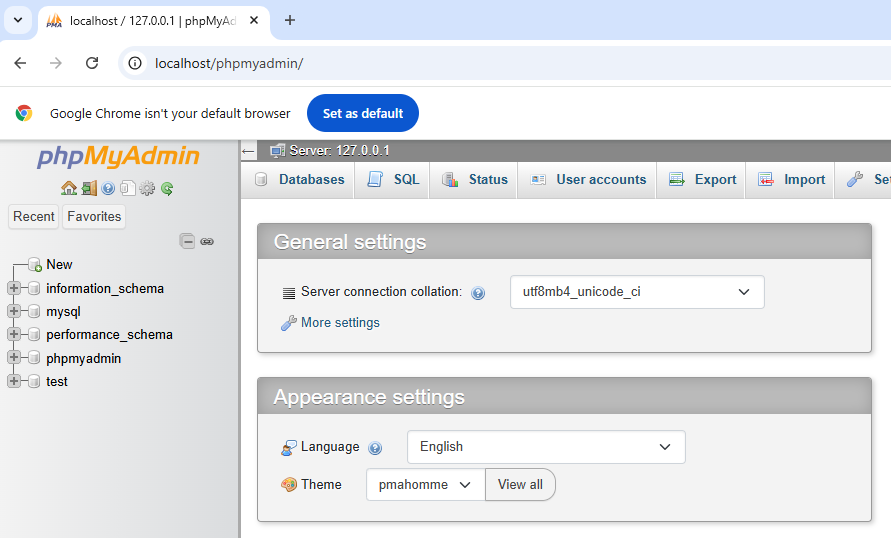
Open your browser and go to localhost/phpmyadmin.
Click on “New” in the left sidebar.
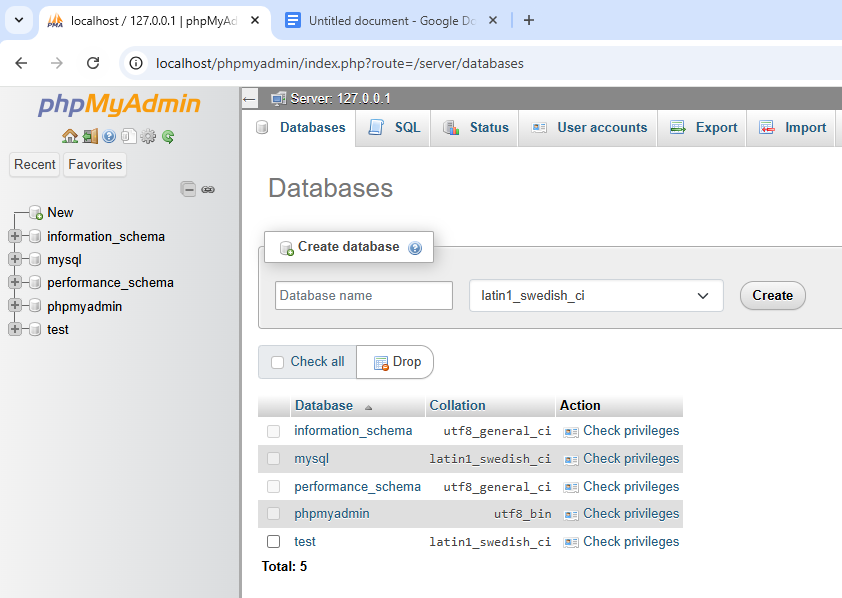
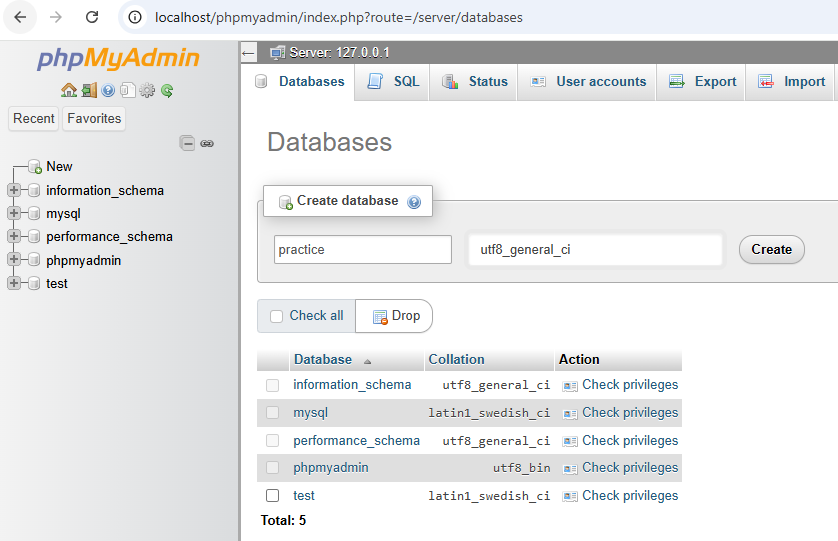
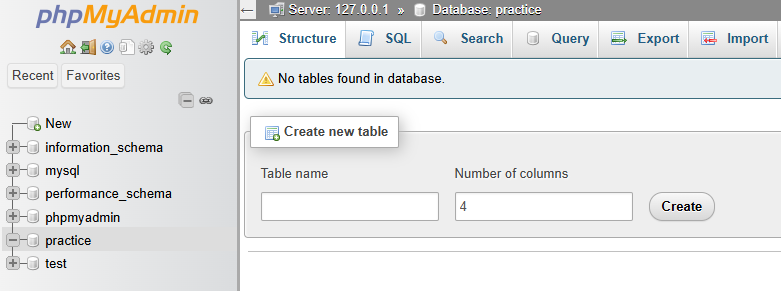
What we’re doing: Setting up a folder to store our PHP project files
Navigate to your XAMPP or WAMP installation folder.
Open the htdocs (for XAMPP) or www (for WAMP) folder. I’m using XAMPP, so I’ll open the htdocs folder.
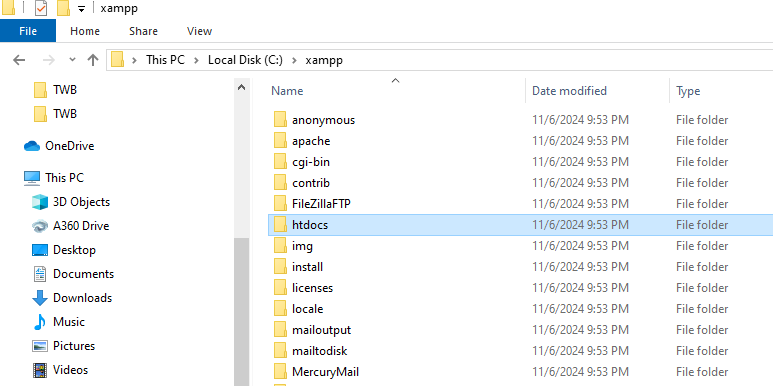
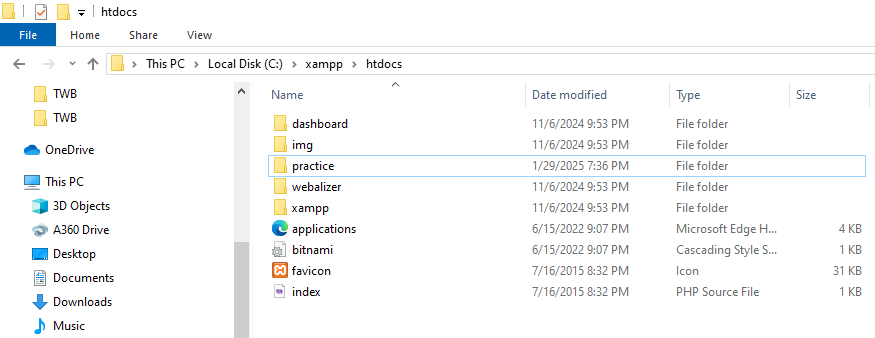
What we’re doing: Writing PHP code to connect to MySQL
Inside the practice folder, create a new file named db_connection.php. Make sure the file extension is .php, not .txt. To verify, click View in the top menu and enable File name extensions (if using Windows).
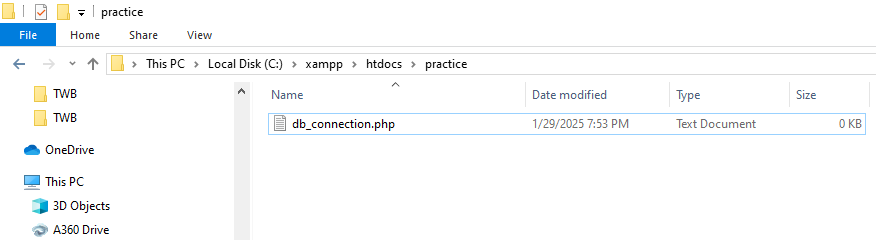
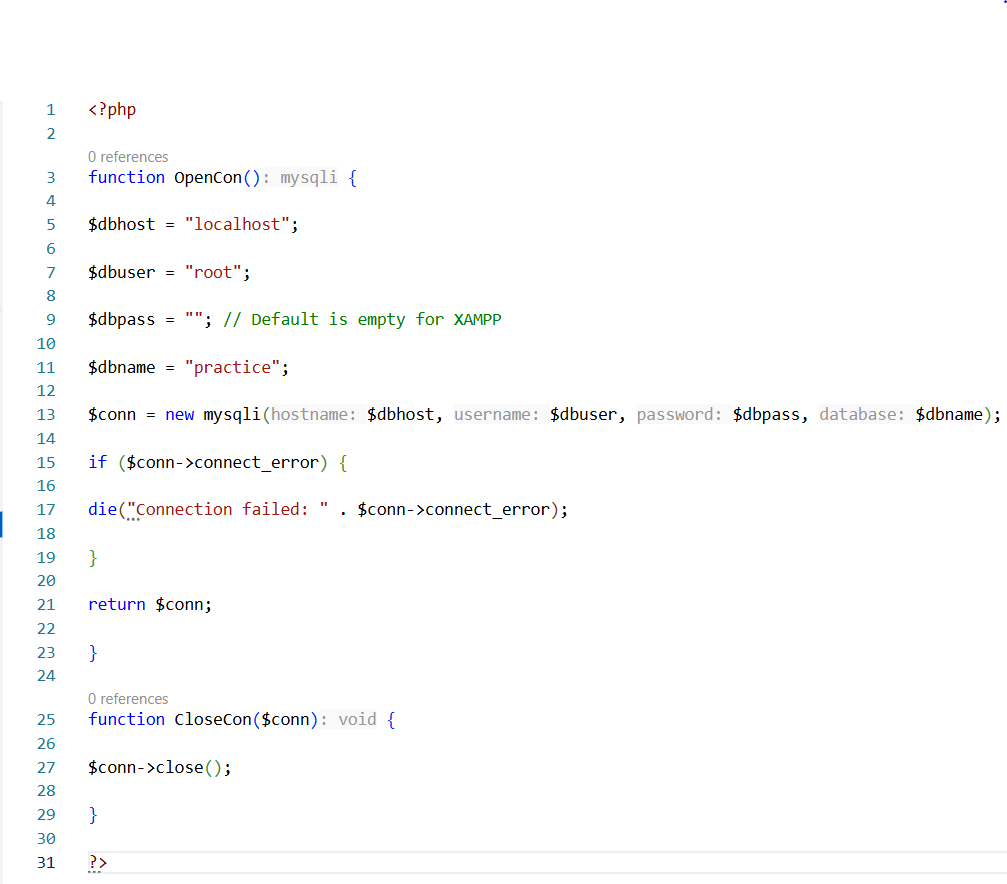
In conclusion, PHP and MySQL remain a powerful and cost-effective combination for web development. Their open-source nature, ease of integration, and strong community support make them ideal for building dynamic, data-driven websites. PHP's compatibility with MySQL allows for seamless data manipulation, while MySQL offers robust performance and scalability. Together, they enable rapid development with secure and reliable database management. Whether for small projects or enterprise-level applications, this duo continues to be a preferred choice for developers worldwide, thanks to their flexibility, extensive documentation, and proven track record in powering millions of web applications efficiently and effectively