
The ESP32 is a popular and versatile microcontroller developed by Espressif Systems. It is widely used in Internet of Things (IoT) applications due to its built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities, low cost, and robust processing power. Below are some of the key aspects and features of the ESP32:
o Powered by dual-core Ten silica Xtensa LX6 processors.
o Clock speed up to 240 MHz
o Suitable for multitasking.
o Wi-Fi: Supports both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands (in some variants) for wireless communication
o Bluetooth: Supports Bluetooth 4.2 and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), enabling connectivity with a wide range of devices.
o SRAM: Typically around 512 KB.
o Flash Storage: Varies, usually between 4 MB and 16 MB.
o Supports external SPI flash and SRAM.
o Numerous GPIO pins that can be configured for various digital and analog functions.
o Supports SPI, I2C, UART, ADC, PWM, and DAC.
o Designed for energy-efficient applications with multiple sleep and low-power modes.
o Ideal for battery-powered IoT devices.
o Hardware support for cryptography (AES, SHA, RSA, etc.).
o Built-in touch sensors.
o Hall sensor and temperature sensor.
o Home automation systems.
o Smart agriculture tools
o Industrial IoT applications
o Fitness trackers.
o Smartwatches
o Wireless control systems.
o Sensor integration for autonomous devices.
o Makers and hobbyists frequently use ESP32 for custom projects due to its flexibility and affordability.
o Used in small-scale data processing at the source (edge) in IoT systems.
The ESP32 can be programmed using various platforms, including:
1. ESP32-WROOM-32: The most common module.
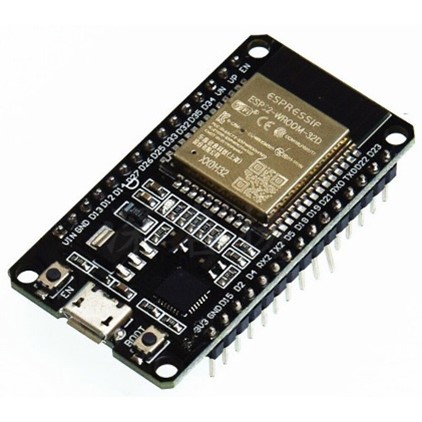

2. ESP32-WROVER: Includes additional PSRAM for memory-intensive tasks.

3. ESP32-C3: Low-cost and low-power single-core RISC-V variant.

4. ESP32-S3: Enhanced AI and ML capabilities with dual-core and improved support for USB OTG.

The ESP32 and ESP8684 cater to different segments of IoT development. The ESP32 stands out as a high-performance platform with extensive features and flexibility, while the ESP8684 offers a lightweight, cost-effective solution for simpler tasks. Developers must choose between the two based on their project's complexity, budget, and power requirements.